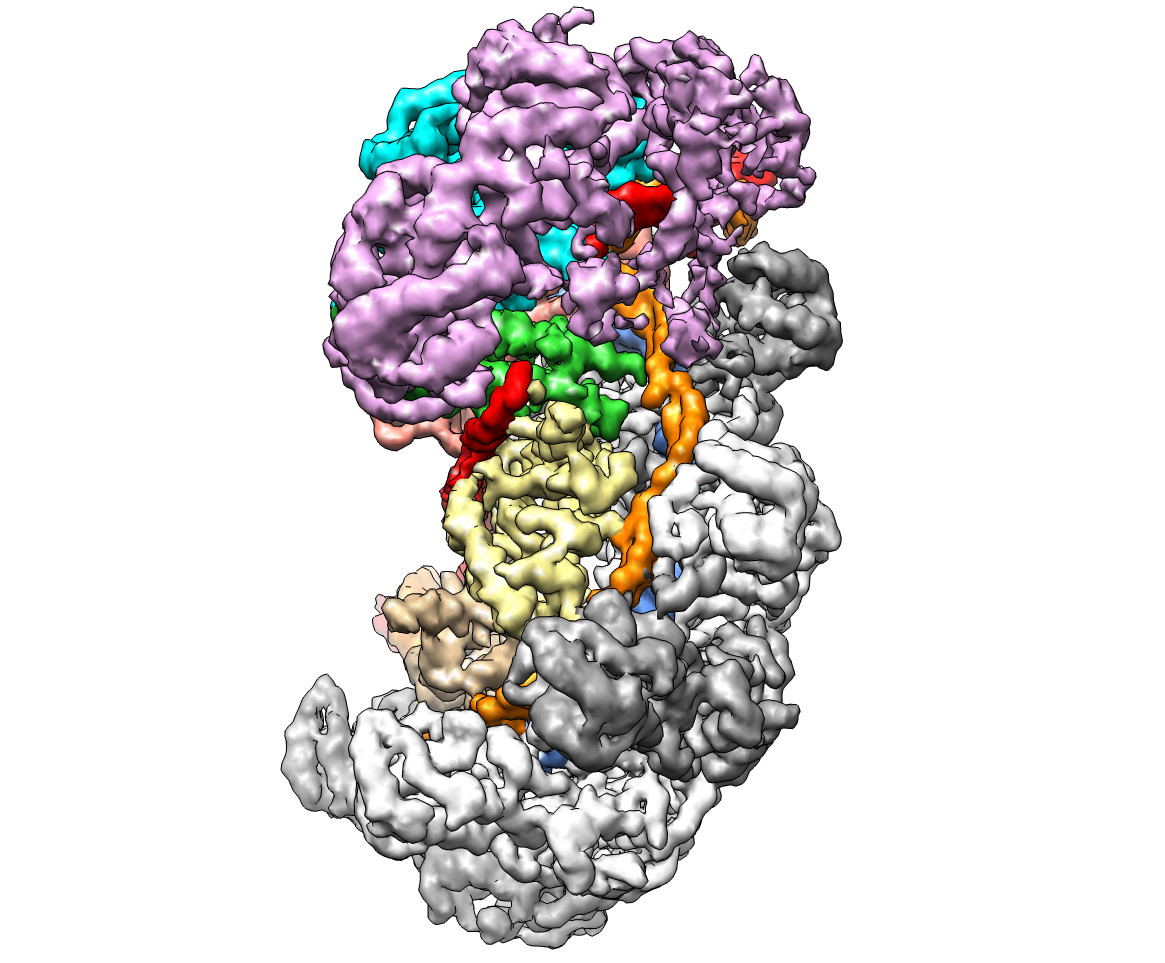
Type I CRISPR-Cas system features a sequential target-searching and degradation process on double-stranded DNA by the RNA-guided Cascade (CRISPR associated complex for antiviral defense) complex and the nuclease-helicase fusion enzyme Cas3, respectively. The Liao lab has used single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to generate a near-atomic resolution structure of the Type I-E Cascade/R-loop/Cas3 complex, poised to initiate DNA degradation. This work, in collaboration with the Ke lab at Cornell University, was published in Science on July 6th. Together with their previous cryo-EM structures of CRISPR/R-loop (Xiao et al, Cell 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.012), their work provides a “molecular movie” that describes the entire course of action for target recognition, single strand nicking, and ATP-dependent DNA processing. The improved structural understanding now enables researchers to work toward modifying multiple types of CRISPR-Cas systems to improve their accuracy and reduce off-target effects in various biomedical applications.