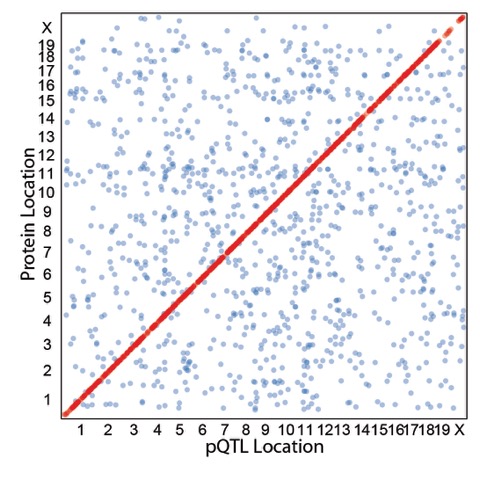
Harnessing natural genetic variants is a powerful tool for introducing genetic perturbations into a model organism. At the Jackson laboratories a cohort of genetic diverse mice known as the diversity outbred mice was created for the purpose of genetic mapping. The mice harbor millions of genetic variants which creates system-wide genetic perturbations in a single population. The Gygi lab, in collaboration with the Jackson laboratories, explored this model to better understand how variants influence protein expression (Chick et al., Nature, 2016). The results from study show that local genetic regulation is mostly dictated by the central dogma. However, distant regulation was almost exclusively through post-transcriptional mechanisms. Their analysis was able to link the abundance of one protein to one or many other proteins revealing many novel protein-protein associations. This approach has a distinct advantage of interactions maps because the association isn’t always dependent on physical interaction.